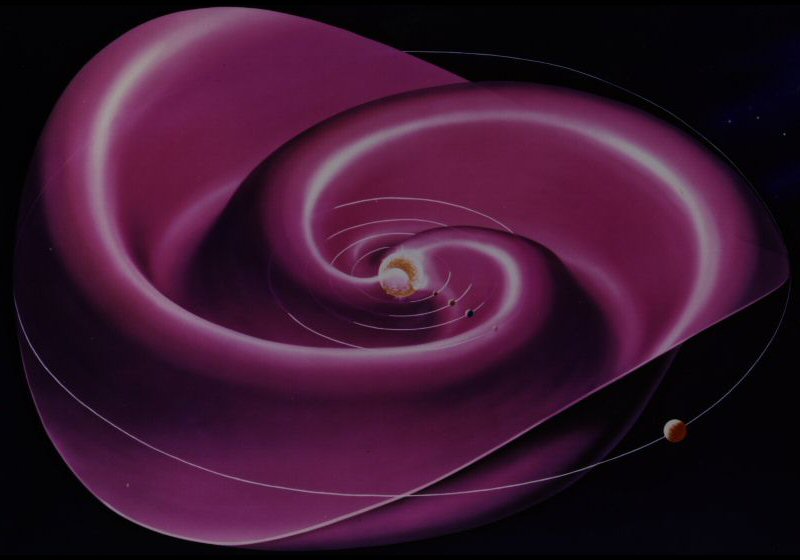
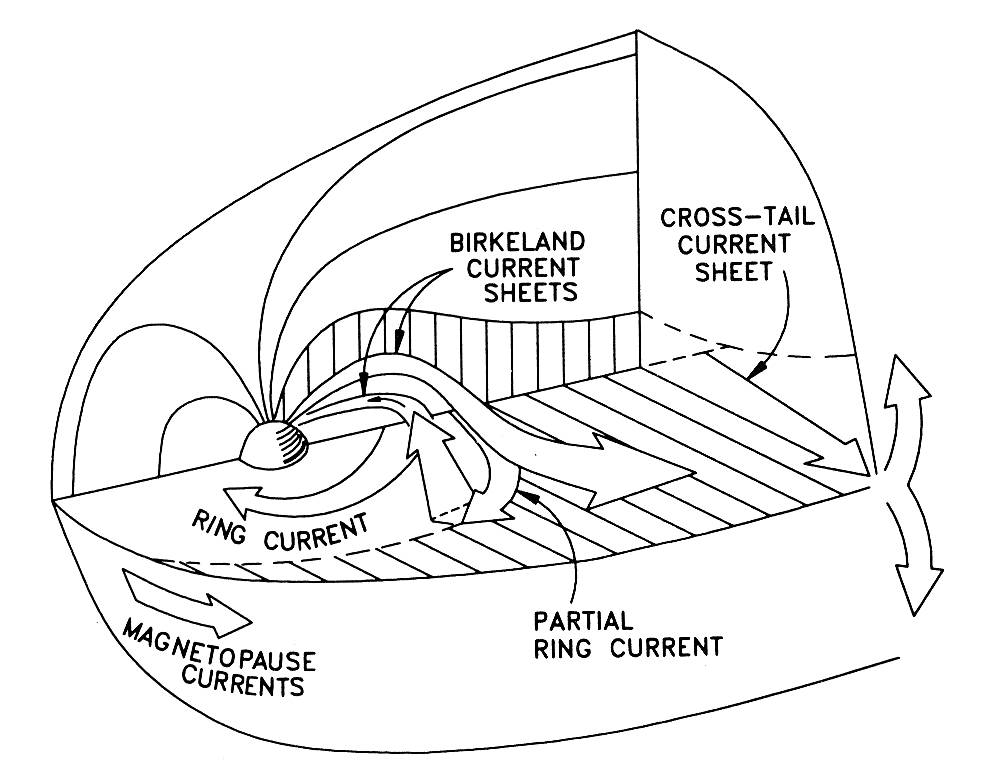
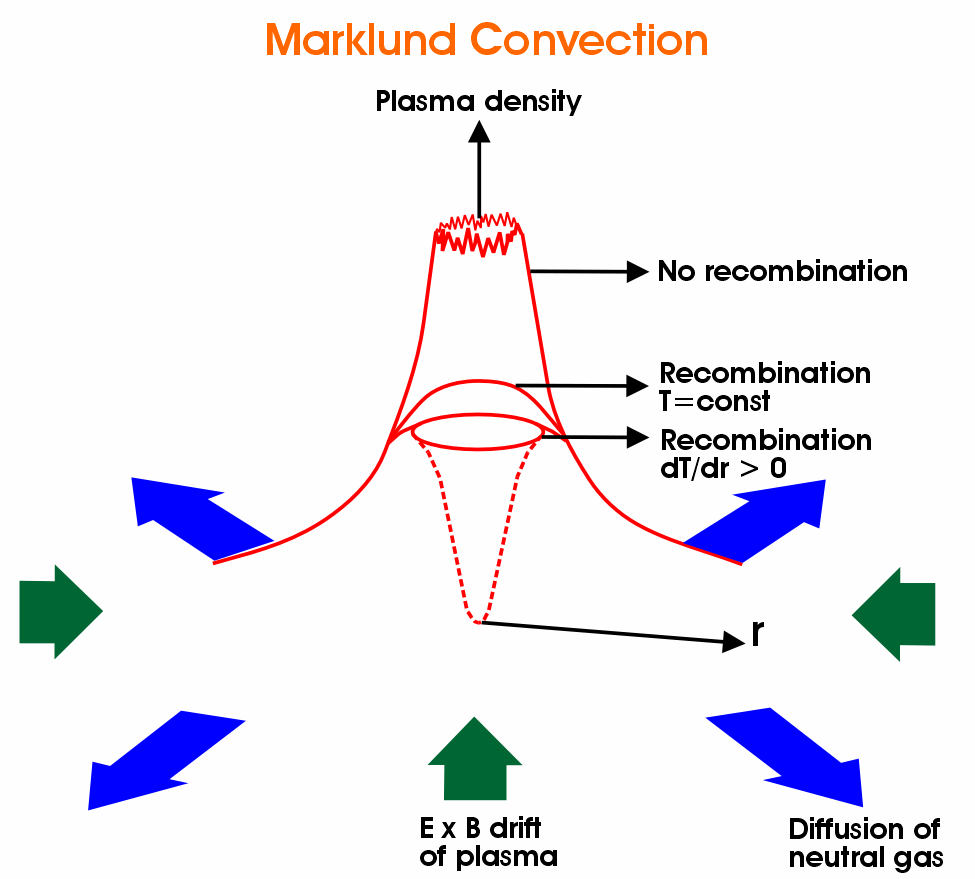
Heliospheric current sheet
The Heliospheric current sheet (HCS) is the surface within the Solar System where the polarity of the Sun’s magnetic field changes from north to south. This field extends from the Sun’s equatorial plane throughout the entire Solar System and is the largest structure in the heliosphere.[1] The shape of the current sheet results from the … Read more