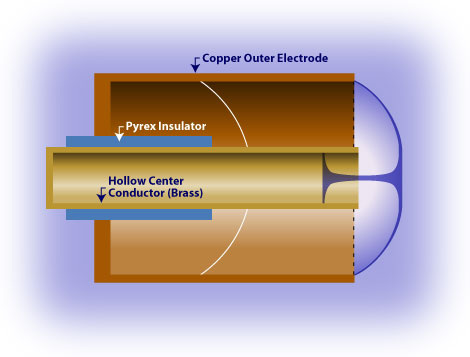
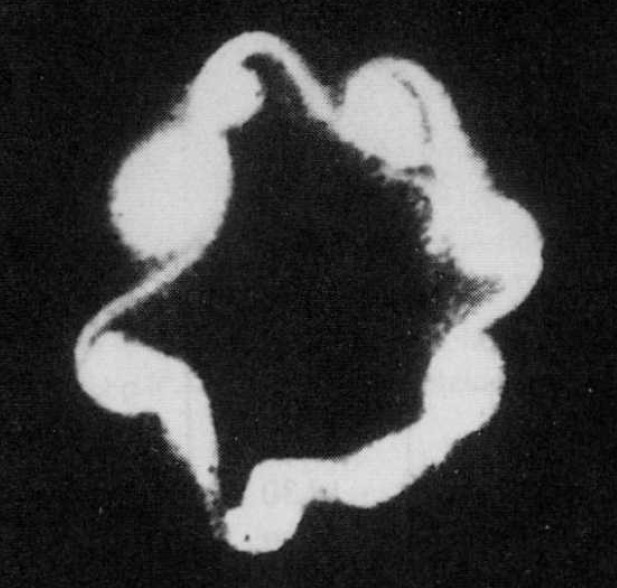
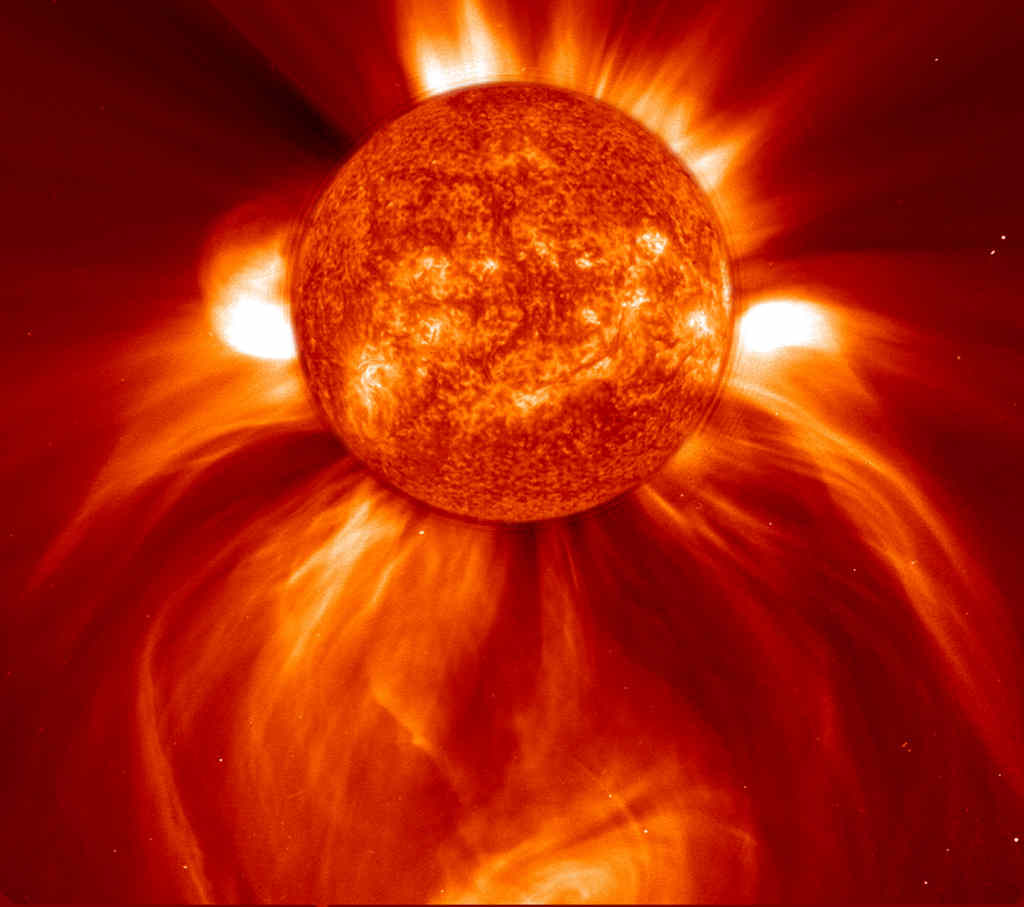
Dense plasma focus
A dense plasma focus (DPF) (also plasma gun) is a plasma machine that produces, by electromagnetic acceleration and compression, short-lived plasma that is so hot and dense that it becomes a copious multi-radiation source. It was invented in the early 1960s by J.W. Mather,[1] and also independently by N.V. Filippov.[2] It is also called a … Read more