A particle beam (sometimes plasma beam, or charged particle beam) is an accelerated stream of charged particles such as electrons and protons, often accelerated towards the speed of light. In the laboratory, such beams are created by particle accelerators such as cathode ray tubes, cyclotrons, and the dense plasma focus. In nature, particle beams are created by electric fields (which accelerate charged particles in opposite directions), such as those in double layers and Birkeland currents.
In the lab, beams are often directed by electromagnetic fields and focused by electrostatic lenses. In nature, the beam is maintained by self-generating magnetic fields, that produce a plasma pinch. One of the characteristics of particle beams, is synchrotron radiation resulting from the loss of energy from electrons moving through magnetic fields.
Laboratory produced particle beams typically require high energies, and are often associated with esoteric weapons research (eg. plasma focus = plasma gun)
Interplanetary particle beams
Interplanetary particle beams have also been reported, the most frequently observed beams are consist of electrons, most of these beams originate from sun flares. [1]
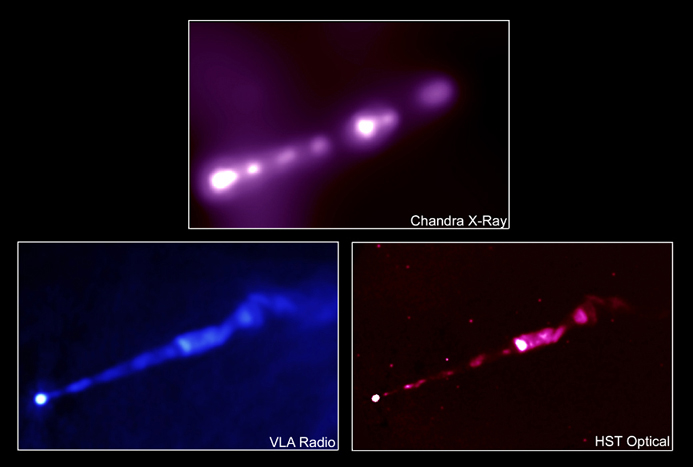
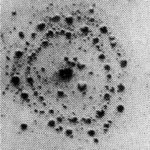
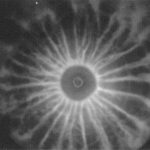
Particle beams in the laboratory and in space
Particle beams in the laboratory (left) and the cosmos (right)
Notes
- ↑ Dulk, G. A., “Interplanetary particle beams“, FULL TEXT Committee of European Radio Astronomers, SNSF, URSI, et al., Workshop on Particle Beams in the Solar Atmosphere, Braunwald, Switzerland, Aug. 21-25, 1989) Solar Physics (ISSN 0038-0938), vol. 130, Dec. 1990, p. 139-150.
- ↑ Winston H. Bostick, “What Laboratory-Produced Plasma Structures Can Contribute to the Understanding of Cosmic Structures Both Large and Small”, IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science Vol. PS-14 No.6 (Dec 1986) (Abstract) PEER REVIEWED
- ↑ Manchanda, R. K.; Sood, R. K.; Waldron, L., “A model for radio emission from SN 1987A”, Astronomy and Astrophysics (ISSN 0004-6361), vol. 211, no. 2, March 1989, p. 353-355. Paper FULL TEXT PEER REVIEWED
Reference
- Andre Gsponer, “Physics of high-intensity high-energy particle beam propagation in open air and outer-space plasmas” (2004)
- Peratt, Anthony L., “The role of particle beams and electrical currents in the plasma universe“, Laser and Particle Beams (ISSN 0263-0346), vol. 6, Aug. 1988, p. 471-491. Paper FULL TEXT PDF PEER REVIEWED
- Borovsky, J. E., “Parallel electric fields in extragalactic jets – Double layers and anomalous resistivity in symbiotic relationships” FULL TEXT (1986) Astrophysical Journal, Part 1 (ISSN 0004-637X), vol. 306, July 15, 1986, p. 451-465. NASA-DOE-supported research. PEER REVIEWED
- Borovsky, J. E., “Double layers and plasma-wave resistivity in extragalactic jets – Cavity formation and radio-wave emission” (NASA, Conference on Double Layers in Plasmas, Huntsville, AL, Mar. 1986) Laser and Particle Beams (ISSN 0263-0346), vol. 5, May 1987, pt. 2, p. 169-175. NASA-DOE-supported research. PEER REVIEWED